Budka, P. (2023). Cultural dimensions of digital ethics: Anthropological notes and perspectives. Presentation at Academies for Global Innovation and Digital Ethics (AGIDE) Workshop, Vienna, Austria: Austrian Academy of Sciences, 17-18 April.
From the AGIDE workshop brochure:
“The digital transformation is changing the way we live, the way our societies and economies function, and is shifting global power relations. Moreover, it has brought about an unprecedented degree of global interconnectedness. In cooperation with other Academies of Sciences worldwide, Academies for Global Innovation and Digital Ethics (AGIDE) seeks to embrace the socio-cultural variety of perspectives from all over the world and to further explore differences and similarities without forcing uniformity or consensus. The first AGIDE workshop will focus on the main questions of the project, that is, how various regions and cultures experience digitalization and whether particular ethical challenges arise due to various cultural dimensions. A series of renowned international speakers were invited to investigate, beyond stereotypes, in which ways cultural dimensions influence how technologies are welcomed, perceived and dealt with. Three main questions were were identified to guide the discussions at the workshop:
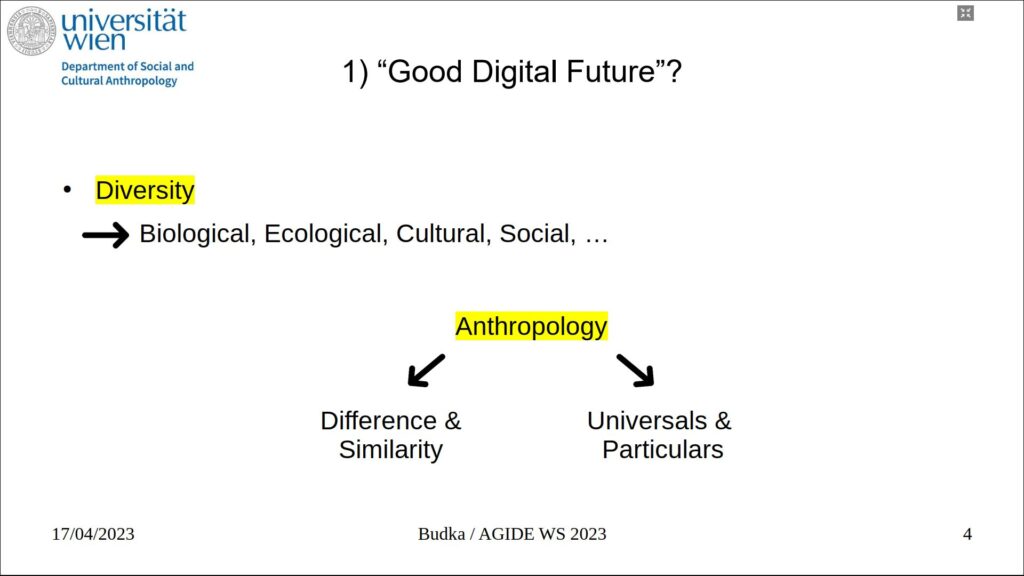
1) What is your vision of a ‘good digital future’ within your cultural context or region?
2) When you step out of the ‘bubble’ of the expert community, what are the views of lay people you meet ‘outside’?
3) What is the most annoying cultural stereotype with regard to approaches to digitization? Why do you find it annoying and what would you change about that stereotype?”
I commented on these questions by providing an anthropological perspective.